Defect detection and classification in welding using deep learning and digital radiography
Abstract
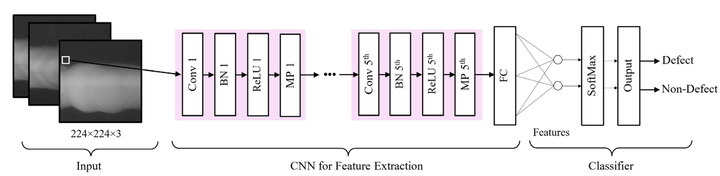
Continuous and digitized monitoring and automated inspection are key parts of modern manufacturing and sustainment of aging infrastructure. The growing demand for these needs and shortage of required skill sets can slow down the global economy by increasing the risk or costs associated with catastrophic events. The diversity of requirements and specialized standards and codes around the world, along with the time-sensitive aspect of such inspections, makes automated fault detection and classification a prime application for utilizing artificial intelligence as an assistive tool that not only automates repeated tasks but also provides users with supporting inference to increase confidence before and during the inspection operation. In most critical cases, non-destructive testing (NDT) must be done once immediately after the weld is created and then on a scheduled or unscheduled repeated basis as the weld ages. One of the most commonly used NDT methods is radiography imaging using penetrating gamma or X-ray radiation. Existing assisted defect recognition tools in the literature are heavily focused on high-quality X-ray images and laboratory-focused imaging parameters, which in many cases are not representative of imaging done in real-world applications. Moreover, the literature has focused on welds that have undergone aging and have very clear defects—problems that classical image processing could easily address. This chapter and demonstration reviews the application of deep learning to find defects in newly created welds with minimal defect size and field-quality manually done welds as opposed to laboratory welds and addresses the industry standards for the classification of discontinuities (defects). First, the work developed and contextualized more than 100,000 X-ray images from various welds and annotated them with a group of NDT experts with varying years of experience. Based on this data and annotations, an optimized convolutional neural network (CNN) was designed and trained for detecting discontinuity and defects. Performance of the designed CNN was tested against other CNN architectures, and the overall accuracy of 96% overall classes was achieved.